Hyperglycemia – Causes, Symptoms, and Management
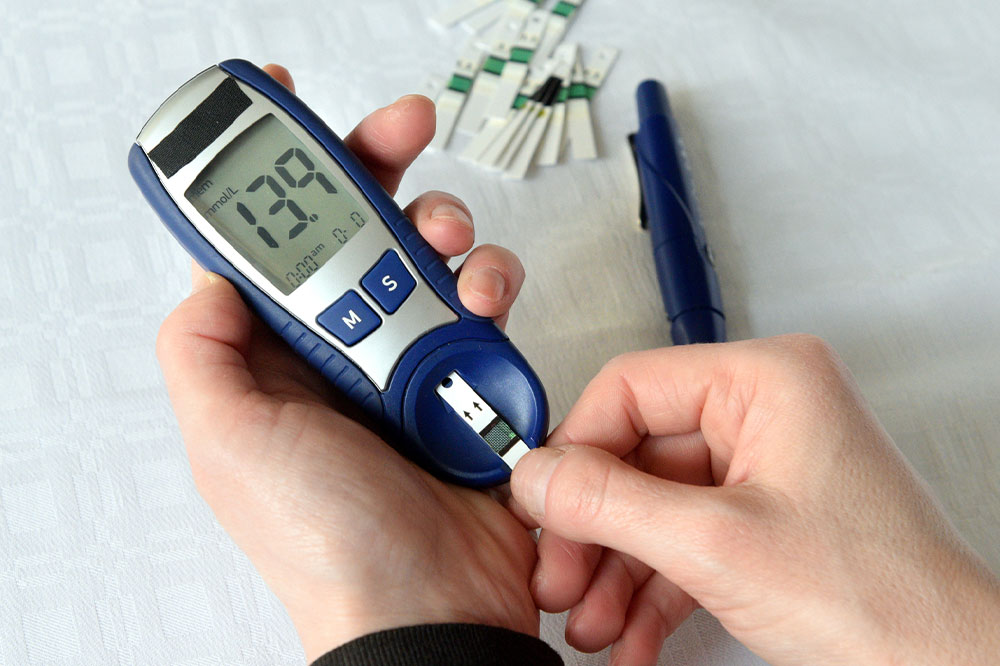
Hyperglycemia is high blood sugar, a complication observed in people with diabetes. It develops when the body has significantly less insulin than required or when the body is unable to process insulin. A person with hyperglycemia usually has a blood glucose level of more than 125 mg/dL when fasting and over 180 mg/dL after eating. When hyperglycemia is left untreated for a long time, it can damage the nerves, organs, and blood vessels.
Causes and risk factors
Many factors can increase the risk of hyperglycemia in people with diabetes. Some of them are:
- Insufficient or inaccurate dosage of insulin that one takes to manage diabetes
- Body’s inability to effectively utilize insulin treatment
- Excessive carbohydrate intake
- Leading a sedentary lifestyle
- Physical or emotional stress
- Dawn phenomenon, which is a hormonal surge or rise in blood sugar people with diabetes experience every morning
Some of the other possible causes of hyperglycemia:
- Cushing’s syndrome results in insulin resistance
- Being affected by pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, and pancreatic cancer
- Using certain treatment options
- Experiencing trauma or surgery
Some of the risk factors of high blood sugar are:
- A family history of diabetes
- Unhealthy lifestyle
- High cholesterol
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome
- History of gestational diabetes
Symptoms
Hyperglycemia may not exhibit symptoms unless one experiences extremely high blood sugar levels, for instance, blood glucose over 180 mg/dL. The symptoms start developing over several days or weeks. The longer one has high blood sugar levels, the more severe the symptoms. If it remains undetected for a long time, a possible complication is a diabetic coma or ketoacidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis or DKA and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome develop as a complication of high blood sugar levels. As this is a serious complication, one should contact a doctor when they notice any such issues. When affected by DKA, ketone levels increase in the blood and urine, mainly in people with type 1 diabetes. So, it is essential to understand the early symptoms of hyperglycemia, especially when one is affected by diabetes. Here are some common symptoms one might experience:
- High blood sugar
- Headache
- Blurry vision
- Feeling excessively hungry or thirsty
- Frequent urination
- Changes in appearance
- Weakness
- Vaginal and skin infections
Management options
If one notices one or more symptoms of high blood sugar, they should consult their healthcare provider regarding proper management techniques. Doctors can also offer guidance regarding how various treatment options can help keep blood glucose in check. If affected by diabetes, one should avoid missing a dose and follow the doctor’s instructions. The treatment for hyperglycemia is determined by factors like the frequency and severity of one’s blood sugar. Other factors include one’s age and health, and mental health. Here are a few management options for the condition:
Lifestyle changes
One’s lifestyle is one of the crucial factors taken into consideration when developing a treatment plan for hyperglycemia. This includes understanding one’s overall physical and mental health and introducing healthy eating habits. Healthcare experts may also recommend staying active. Additionally, keeping an eye on one’s blood sugar levels is crucial. Further, treatment for diabetes is influenced by one’s lifestyle and will not be entirely effective if one does not make better choices.
Healthy eating habits: A carbohydrate-rich meal plan can have a huge impact on one’s blood sugar. So, choosing sugary foods and beverages on a regular basis can increase the risk of developing hyperglycemia. So, it is essential to make changes to one’s meal plan to limit carbohydrates and added sugar and instead opt for fiber-rich food.
Regular exercise: Avoiding a sedentary lifestyle or long periods of sitting or sleeping can help prevent diabetes. Regular physical activity can help in achieving glycemic control when one is dealing with diabetes, as exercising lowers blood sugar levels. So, one can go for a walk after having a big meal to help them burn calories and excessive sugar in the blood. Regular workout also helps improve one’s overall health. But before one introduces drastic changes in their daily routine, it is important to consult a healthcare professional.
Monitoring blood sugar: Regularly monitoring one’s blood sugar is a crucial step in diabetes management. Keeping track of one’s blood glucose also helps in evaluating the effectiveness of treatment options and lifestyle changes. Understanding the pattern of spikes in one’s glucose levels helps one manage and even prevent hyperglycemia.
Treatment options
While eating habits and lifestyle can help one avoid high blood sugar, certain prescriptions are required to keep blood glucose in check. The common options would include:
Insulin therapy: This is a hormone that controls the level of blood sugar in the body. When affected by type 1 diabetes, the body cannot produce enough insulin. So, one would have to take regular insulin doses to deal with the disease.
Other prescription options: Along with insulin, adjunctive treatments can help control the blood sugar level when dealing with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Other oral options can also help with controlling blood glucose.
Emergency treatment
If one experiences severe symptoms like diabetic ketoacidosis, they will have to be rushed to the hospital and get immediate treatment. Emergency treatment focuses on lowering blood sugar and bringing it back to the normal range. Here are the methods doctors usually use:
Fluid replacement: Here, one receives fluids intravenously until the body gets back all the fluid they might have lost due to frequent urination. Fluid replacement also assists in diluting the extra amount of sugar in the blood.
Electrolyte replacement: Electrolytes are minerals in blood that are essential for the tissues to function correctly. When there is a lack of insulin in the body, one might also experience a decrease in the blood’s electrolyte levels. So, here one will receive electrolytes through veins.
High blood sugar is a common concern in people with diabetes, however, healthy eating habits, an active lifestyle, and regular check-ups can help one avoid serious complications. Further, recognizing the early signs and risk factors of developing hyperglycemia is also a crucial step in managing diabetes.